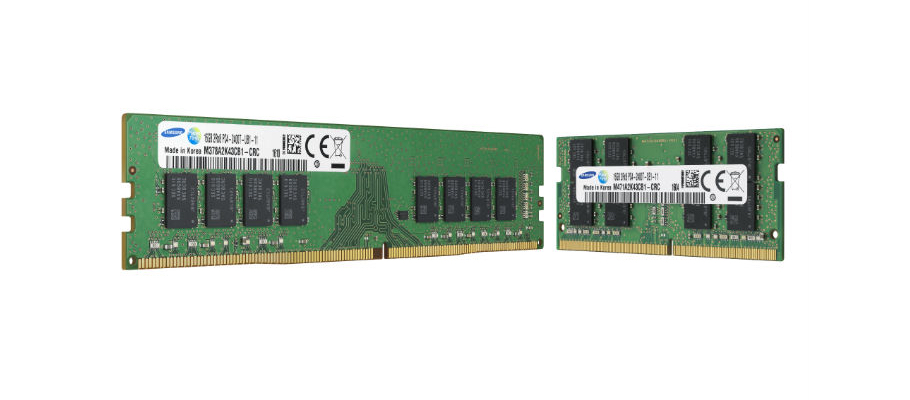
Samsung has seen a decline in DRAM sales and profit, though that could change later this year, but the company has committed itself to consuming more time with NAND flash that has proven it is the better option of the two with faster read/write speeds. Now, though, the company that is bringing UFS-based microSD cards to the industry has partnered with IBM to break another inevitable trend: that of NAND flash dependence.
Samsung and IBM have published a paper detailing their advancements in Spin-Transfer Torque Magnetoresistive RAM (or STT MRAM) that has resulted in smaller-sized chips to be used in wearables and IoT devices. STT MRAM is small and can fit inside wearables (which are relatively small when compared with most high-end electronics), uses zero power when idle due to its resistance, and can likely outlast current memory chips. STT MRAM also boasts faster read/write speeds, with NAND flash requiring 1 microsecond to write data as opposed to STT MRAM's 10 nanoseconds. This new MRAM development could result in the eventual replacement of DRAM, despite the fact that upcoming devices such as Samsung's Galaxy Note 7 will still pay homage to the old guard. While DRAM replacement may take a while, embedded flash could be substituted in a much quicker fashion.
You can find out more about STT MRAM and its potential at the link below.